Twitter as well as Square CEO, Jack Dorsey recently stated “Africa will certainly specify the future (specifically the Bitcoin one!)” Was he?
Previously this year, Luno published The State of Crypto in Africa record in partnership with Arcane Research. This was an effort to comprehend where the future for crypto in Africa is headed.
In this recap, we’ll highlight a few of the crucial elements of the study, consisting of the stimulants for crypto fostering in Africa, challenges to be conquered, and the most up to date fads.
Crypto in Africa on the Rise
Depressing to be leaving the continent … for currently. Africa will define the future (specifically the bitcoin one!). Uncertain where yet, however I’ll be living below for 3-6 months mid 2020. Grateful I was able to experience a small part. pic.twitter.com/9VqgbhCXWd
— jack (@jack) November 27, 2019
Crypto in Africa
In spite of being an extremely diverse continent, African countries usually share vital resemblances, varying from socio-economic problems to a substantial lack of framework. Making use of cryptocurrencies worldwide has, to date, mostly centred on investment, trading as well as speculation. This is not true of Africa, where applications for crypto and the range of challenges it can help get over vary far a lot more.
This makes it a productive reproduction ground for crypto. As the record notes that “Africa is one of, if not the most encouraging area for the adoption of cryptocurrencies.
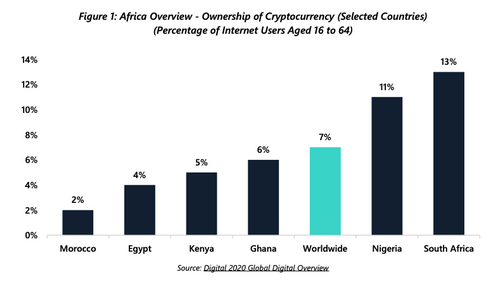
There’s currently a polarity to crypto fostering in Africa. On the one hand, researchers have recognized high possession prices in specific countries. Google Trend data suggests Uganda, Nigeria, South Africa, Kenya and also Ghana all rank in the leading 10 on the subject of cryptocurrency, which shows the expanding passion therein. South Africa in fact placed third-highest worldwide at 13% with Nigeria ranking 5th (11%) in a survey regarding crypto ownership.
In regards to crypto framework, though, it’s lagging behind. There’s still an unique lack of nodes, mining operations and also supporting merchants. Of the 10,267 Bitcoin nodes worldwide, just 20 (0.2%) are located in Africa. Additionally, study from CoinShares shows there’s virtually no meaningful Bitcoin mining task across Africa.
Trading fads
Trading volumes throughout non-P2P (peer to peer) exchanges suggest there is typically less than $10 million in day-to-day trading quantity across African currency pairs. Luno adds to the majority of this volume.
On the other hand, Africa make up a somewhat much bigger share of the P2P trading market. Trading across Africa currently represents greater than 14% of LocalBitcoins’ and also Paxful’s global once a week trading quantities, with activity focused in Nigeria, Kenya and also South Africa. These quantities have seen a significant boost in 2020, exceeding $10 million in weekly quantity across the 2 platforms.
Catalysts for fostering
Africa’s underdeveloped crypto facilities aside, there are a variety of major drivers that can be helpful to extensive adoption over the following years. A number of these are special to the African continent, showcasing an impressive chance for jobs that have the ability to take advantage of the possibility.
Economic landscape: high inflation as well as financial instability
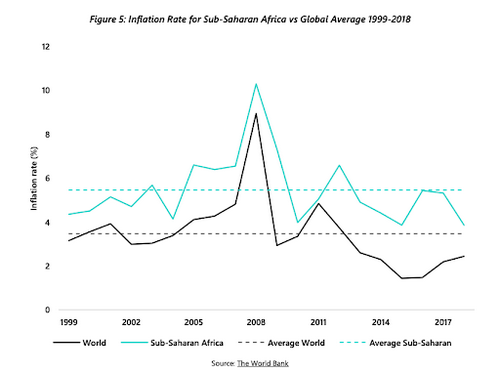
Most of African nations struggle with high inflation rates– traditionally a lot greater than the global average. This significantly threatens purchasing power as well as the potential for wealth-gain. Bitcoin’s inherently disinflationary financial design as well as decentralised governance therefore presents an appealing choice.
In the very same vein, many African countries experience diminishing as well as often unpredictable nationwide money. The South African Rand (ZAR) has actually shed over 50% of its value versus the US Dollar, while also being one of the most volatile FX currencies.
Political instability as well as funding control
Most African nations experience from large political instability which worsens inflation and currency volatility. Data from the World Bank offers just nine of the 53 African countries with a favorable rating on the political instability index.
Bitcoin and also other cryptocurrencies are special in that they combine the riches preservation buildings of hard properties, like gold and also land, with the portability of digital currency, integrated with an unequaled level of censorship resistance. These residential properties, in mix, make cryptocurrencies the suitable antidote to political chaos.
Financial infrastructure
The majority of Africa is underserved by traditional economic services. The number of industrial banks per 100,000 grownups is 61% lower throughout Sub-Saharan Africa than the international standard. Since 2018, 66% of those residing in Sub-Saharan Africa had no accessibility to a traditional checking account.

Inadequate financial services as well as restricted access inhibit entrepreneurship, organization saving, borrowing and development. These all job to drastically undermine economic development. Cryptocurrencies and decentralised finance (DeFi) are positioned to handle the obstacle of supplying people with a risk-free location to store as well as interact with their money.
Cross-border repayments as well as expensive compensations
Cryptocurrencies provide a much easier and often less expensive option to compensation settlements. Compensations below $200 to Sub-Saharan nations set you back approximately about 9% compared to the international standard of 6.8%. These inflated prices are a mix of an ineffective uncompetitive financial market as well as a dependence on tradition monetary communications systems, such as SWIFT.
Compensations are very crucial in Sub-Saharan Africa and comprise a key element of economic earnings. It’s estimated that over 25 million people are expats from Sub-Saharan Africa as of 2017. This group remitted greater than $48 billion in 2019.
Digital as well as mobile fads
In spite of improvements to standard financing infrastructure, more exponential development would call for considerable financial investments. With practically 60% of the Sub-Saharan population living in backwoods, mobile as well as digital solutions are far extra furnished to deal with concerns to access. Unlike other areas, several African nations have actually leapfrogged traditional financing entirely, going straight to mobile financial. This trend is ideally fit to cryptocurrency fostering.
Mobile settlements
M-Pesa’s success works as one of the very best examples of the expanding prominence of mobile finance. Having actually debuted in 2007, it now has more than 37 million energetic individuals, processing 11 billion transactions annually.
21% of Sub-Saharan Africans currently utilize a mobile money service, with even more individuals of mobile accounts than traditional savings account. A big disadvantage to mobile cash services, though, is the hefty cost tag with a standard of 2% of a transaction’s complete worth. Crypto, on the various other hand, provides much more affordable fees.
Unlike mobile money options, which are generally operable on standard gadgets, a lot of cryptocurrency wallets just function on smart devices. Even though Sub-Saharan Africa drags the global standard in terms of mobile phone usage, the fostering rate is quickly expanding. While there were 250 million smart device connections in 2017, making up 34% of total phone links, this is forecasted to enhance to 690 million in 2025, with mobile phones representing 67% of phone connections
Challenges to conquer
Along with the powerful stimulants anticipated to drive crypto fostering, there are a variety of major obstacles to be gotten rid of. A few of the most widespread are poor web insurance coverage, competition from mobile money solutions and also hostility from governments.
Inadequate web protection
Unlike mobile money services, most cryptocurrency pocketbooks require web connectivity to send out as well as get transactions. Just 39.9% of the African populace have some form of web accessibility, compared to 62.9% throughout the remainder of the globe. 7 African countries have internet infiltration rates listed below 10%. A UN record just recently estimated that an incredible $100 billion of further investment over the following 10 years to boost protection to a sensible requirement.
The lack of insurance coverage can be connected to an absence of infrastructure and also resulting high prices. Sub-standard power supplies are extra adding elements. Numerous African countries have actually distributed populaces, commonly with reduced ordinary incomes, which indicates there’s less financial motivation for business to buy infrastructure growth. This results in a savage cycle of inadequate connection as well as economic underdevelopment. Therefore, telecoms drivers conspire and also monopolise on rates, undermining African citizens. Throughout the continent, 1GB of information usually costs 7.12% of an individual’s regular monthly salary, reaching as high as 20% in some nations.
Satellites as an option
Over the previous few years, the satellite industry has grown significantly. Companies like SpaceX, Amazon, Viasat and also OneWeb are developing low-orbit satellite mega-constellations that intend to give high-speed internet throughout the globe. These will certainly be specifically useful in remote and also country areas.
Sending BTC without web
There’s likewise an increasing emphasis on the transmission of crypto settlements without net connectivity. To date, Blockstream has actually been the pioneer in this field, developing a satellite connect with worldwide insurance coverage that relays the Bitcoin network for cost-free.
Blockstream signed up with pressures with one more decentralised communications business, goTenna, which permits users to transmit deals without web by means of its mesh network. It’s anticipated that satellite web could complete with more conventional approaches in the coming years.
Poor electricity coverage
Beyond web connectivity problems, inadequate electrical power protection provides one more obstacle. A jaw-dropping 57% of the populace across the Sub-Saharan area still lacks accessibility to electricity.

Competition from mobile money suppliers
The success mobile cash services have appreciated in Africa is a double-edged sword to crypto adoption. Fostering might battle when faced with such prominence because of business moats and also network results that have actually developed. Nevertheless, these solutions have actually made individuals more comfy with as well as accustomed to digital and mobile repayment remedies, which can pave the means for different and extra cost-efficient solutions like cryptocurrency pocketbooks.
While mobile cash services depend on a centralised company version to run, extracting fees and income from clients, cryptocurrencies can take on raised capability minus the minimal expenses.
Although Bitcoin as well as Ethereum blockchains might not be as affordable, various other choices like Ripple, Bitcoin Cash and Stellar can provide on-chain deals for far less. Second-layer remedies like the Lightning Network also have the potential to use almost-free purchases.
Mobile money options have an advantage in the breadth of solutions they supply (return on deposits, insurance policy and fundings) but developments in the DeFI space ought to allow crypto services some market share.
Resistance from regulatory authorities
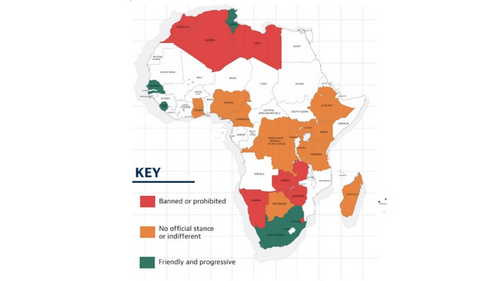
The largest short-term hindrance for cryptocurrencies is unfavourable action from regulatory authorities as well as legislators. The validity of Bitcoin and also various other crypto varies significantly across Africa, with over 60% of African governments yet to clarify their setting.
North African nations have actually taken one of the most hostile positions, with Alergia, Libya and also Morocco having actually all issued bans versus making use of cryptocurrencies. The most common position, however, is among caution. Nations like Kenya, Ghana and Zambia have recommended discernment without actively outlawing them.
Luno’s exchange
Luno appears to be one of the most prominent centralised exchange platform with over 4 million clients. Launched in 2013, Luno has local African hubs in Cape Town, Johannesburg and Lagos and also processes roughly $4.5 million each day generally in 2020, primarily in the South African market. This is mirrored in the overview of Luno’s fiat-to-crypto quantity, where 75% of the trading volume has actually been in South African Rand (ZAR) so much this year.
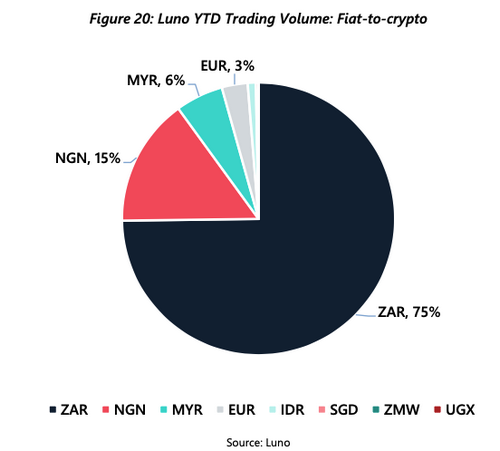
Not just are the African countries controling on Luno’s system, a large portion of the users are also based in these nations (75%).
Seeking to the future
By taking a look at cryptocurrencies not as a financial investment automobile however as a worldwide means of settlement, it’s clear Africa is poised to welcome crypto as an option to much of the consistent concerns the continent deals with. Most, if not all, challenges to mass fostering can as well as will certainly be gotten over following investment in framework as well as the creation of tangible applications that deal with issues one-of-a-kind to the African continent.
Education and learning is an extremely essential facet of the cryptocurrency space. If any brand-new innovation is to be adopted, users require to be equipped with the knowledge to make audio economic decisions for themselves.
While the technical and financial advantages are there, without straight activity as well as a solid understanding on the residents, capacities and also regulatory authorities alike will not be equipped to embrace crypto in any significant method.
South Africa really placed third-highest worldwide at 13% with Nigeria ranking 5th (11%) in a study regarding crypto ownership. Of the 10,267 Bitcoin nodes worldwide, just 20 (0.2%) are situated in Africa. Trading throughout Africa now accounts for more than 14% of LocalBitcoins’ and also Paxful’s worldwide once a week trading quantities, with task focused in Nigeria, Kenya as well as South Africa. The number of commercial banks per 100,000 grownups is 61% lower throughout Sub-Saharan Africa than the international average. As of 2018, 66% of those living in Sub-Saharan Africa had no accessibility to a standard bank account.